MyBatis是一种在Java语言中使用的开源持久化框架,它通过简化数据库访问操作,使开发人员能够更轻松地与数据库进行交互。MyBatis将数据库操作从Java代码中分离出来,通过XML或注解配置来映射Java对象与数据库表之间的关系,从而实现了对象关系映射(ORM)
MyBatis的一些主要特点和组成部分:
易于学习和使用:MyBatis相对于其他ORM框架而言,学习曲线较为平缓。它允许开发人员直接编写SQL语句,从而更加灵活地控制数据库操作
灵活的SQL映射:MyBatis支持在XML配置文件中编写SQL语句,这些SQL语句可以动态生成,根据不同的条件生成不同的SQL查询。这样可以避免过多的重复代码,提高开发效率
支持原生SQL:与其他ORM框架相比,MyBatis更加接近原生SQL,使得开发人员可以更好地优化和调整SQL语句以提高数据库性能
提供映射器(Mapper)接口:MyBatis使用Java接口和映射器文件(XML或注解)来描述数据库操作,使开发人员可以使用简洁的接口定义和调用SQL语句
缓存支持:MyBatis支持一级缓存和二级缓存,可以减少数据库查询次数,提高系统性能
使用MyBatis:在应用程序中调用映射器接口来进行数据库操作
总体而言,MyBatis是一款功能强大且灵活的Java持久化框架,适用于各种规模的应用程序和数据库操作需求。它与Spring等框架集成良好,并在许多Java项目中得到广泛应用
在使用Mybatis的时候,我们只需要定义好Mapper接口,在业务层需要的地方注入对应Mapper即可
@MapperScan @MapperScan 注解属于 mybatis 的扫描包注解,它用于自动扫描指定的包路径,以发现并注册MyBatis的映射器接口(Mapper Interface )。使用 mapperscan可以简化MyBatis的配置过程,特别是在项目中存在多个映射器接口时,可以避免手动一个个地在配置文件中注册这些接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Documented @Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class) @Repeatable(MapperScans.class) public @interface MapperScan {default {};
我们看到了 @MapperScan 注解上 @Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class),这里导入了 MapperScannerRegistrar 类,此类实现了 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口,覆写了 registerBeanDefinitions() 方法,在容器初始化时将 beanDefinition 注册到容器之中
MapperScannerRegistrar 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class MapperScannerRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar , ResourceLoaderAware {@Override public void registerBeanDefinitions (AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {AnnotationAttributes mapperScanAttrs = AnnotationAttributes .fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MapperScan.class.getName()));if (mapperScanAttrs != null ) {0 ));void registerBeanDefinitions (AnnotationMetadata annoMeta, AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String beanName) {BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);"processPropertyPlaceHolders" , true );
后续Spring就会基于这个MapperScannerConfigurer做一系列文章
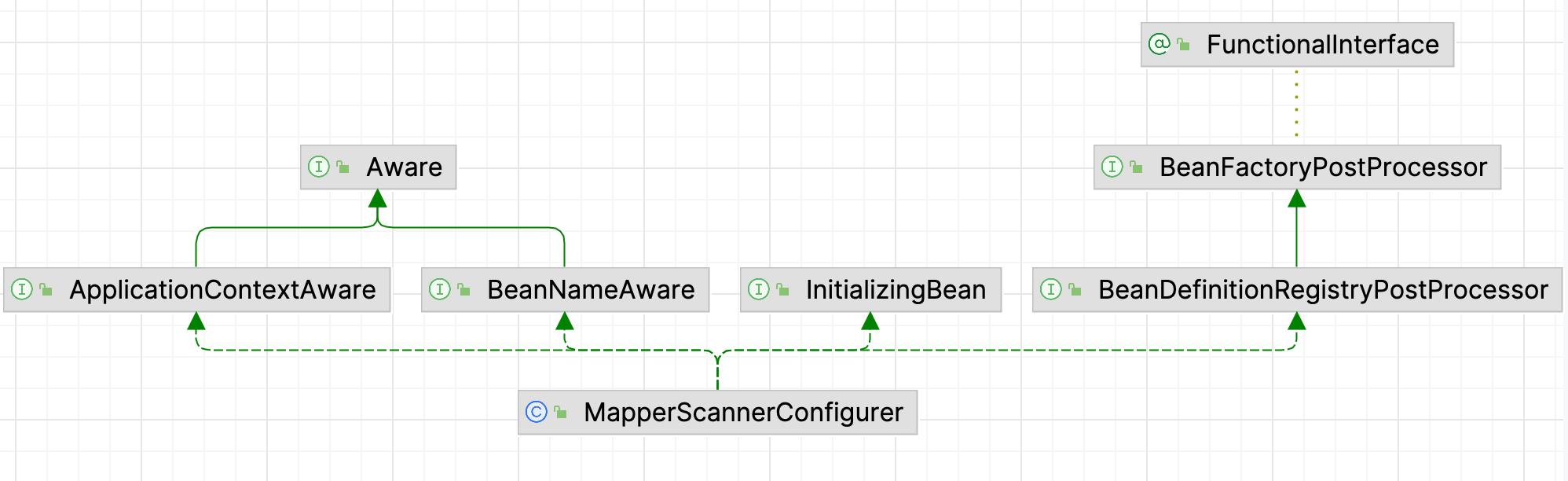
它是 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的实现类,是一个 BeanFactory 后置处理器,Spring启动时回调被覆盖的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 方法来添加beanDefinition的操作,MapperScannerConfigurer这个类中具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry (BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {if (this .processPropertyPlaceHolders) {ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner (registry);this .addToConfig);this .annotationClass);this .markerInterface);this .sqlSessionFactory);this .sqlSessionTemplate);this .sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);this .sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);this .applicationContext);this .nameGenerator);this .mapperFactoryBeanClass);if (StringUtils.hasText(lazyInitialization)) {this .basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
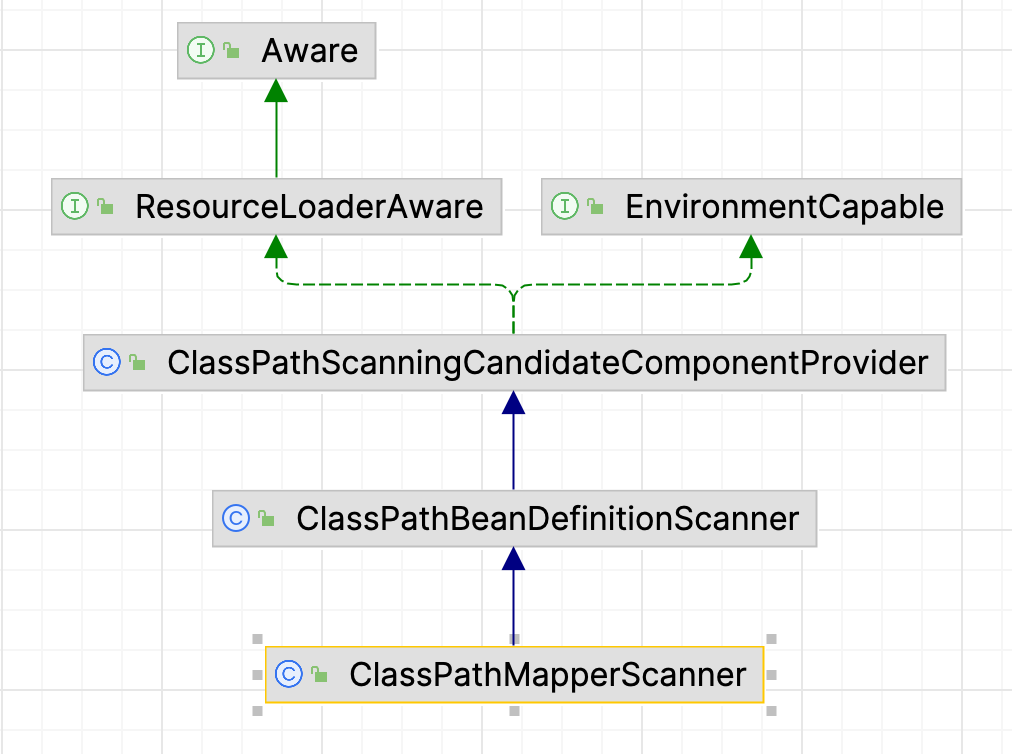
在这个方法中创建了ClassPathMapperScanner对象,然后使用这个扫描器来扫描有Mapper注解的类,看它的关系知道,它是ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的子类,而spring则是使用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner来进行扫描的
ClassPathMapperScanner
ClassPathMapperScanner 通过调用 registerFilters() 方法来添加 includeFilter(实际类型是:TypeFilter ),这里是Spring提供的扩展点,Mybatis定义的是 @MapperScan 注解中 annotationClass 属性配置的注解类型,这里配置了Mapper,所以调用scan()方法开启扫描后,Spring就会将包含Mapper注解的类扫描为BeanDefinition
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 @Override public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan (String... basePackages) {super .doScan(basePackages);if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {else {return beanDefinitions;private void processBeanDefinitions (Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();this .mapperFactoryBeanClass);"addToConfig" , this .addToConfig);if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {@Override protected boolean isCandidateComponent (AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {return beanDefinition.getMetadata().isInterface() && beanDefinition.getMetadata().isIndependent();
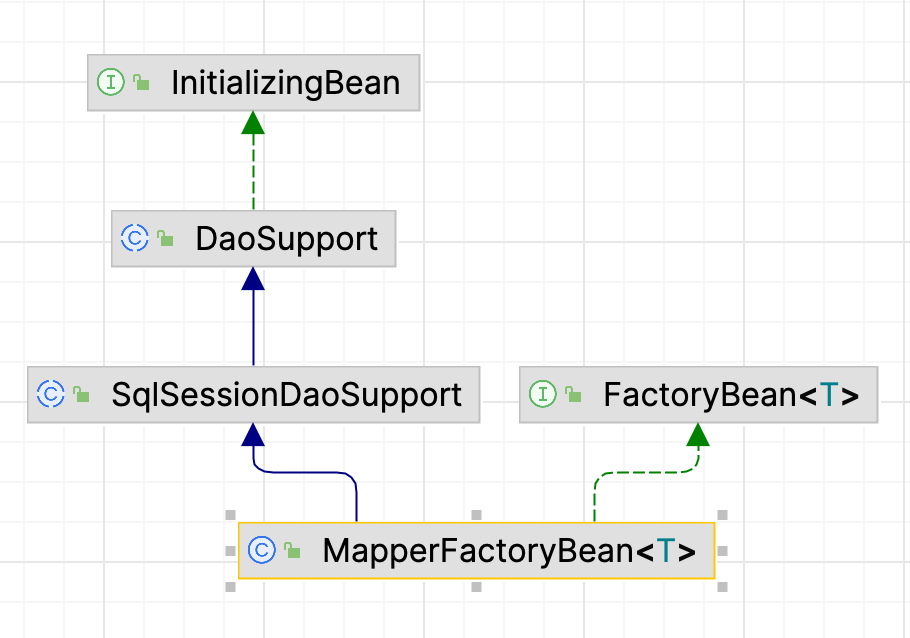
这个 MapperFactoryBean 是 FactoryBean 的实现类,Spring在实例化Mapper时,实际上是实例化MapperFactoryBean ,再调用它的getObject() 方法
MapperFactoryBean 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class MapperFactoryBean <T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean <T> {private Class<T> mapperInterface;public MapperFactoryBean () {public MapperFactoryBean (Class<T> mapperInterface) {this .mapperInterface = mapperInterface;@Override public T getObject () throws Exception {return getSqlSession().getMapper(this .mapperInterface);
MapperFactoryBean 的继承关系:
实现了InitializingBean,继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport,DaoSupport,在DaoSupport里重写了 afterPropertiesSet() 方法执行了checkDaoConfig() 方法;故在MapperFactoryBean初始化完成后,Spring会调用它的afterPropertiesSet()方法,从而会执行到checkDaoConfig()方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override protected void checkDaoConfig () {super .checkDaoConfig();this .mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required" );Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();if (this .addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this .mapperInterface)) {try {this .mapperInterface);catch (Exception e) {"Error while adding the mapper '" + this .mapperInterface + "' to configuration." , e);throw new IllegalArgumentException (e);finally {
该方法调用了 configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface) 方法,然后
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class MapperRegistry {public <T> void addMapper (Class<T> type) {if (type.isInterface()) {if (this .hasMapper(type)) {throw new BindingException ("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry." );boolean loadCompleted = false ;try {this .knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory (type));MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder (this .config, type);true ;finally {if (!loadCompleted) {this .knownMappers.remove(type);
其实就是使用Mapper的接口类型作为key,MapperProxyFactory 作为value,添加到 MapperRegistry 对象Map集合中
实例化 在Spring完成 MapperFactoryBean 的创建后,会调用它的 getObject() 方法来获取真实对象
1 2 3 4 @Override public T getObject () throws Exception {return getSqlSession().getMapper(this .mapperInterface);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public <T> T getMapper (Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {this .knownMappers.get(type);if (mapperProxyFactory == null ) {throw new BindingException ("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry." );else {try {return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);catch (Exception var5) {throw new BindingException ("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + var5, var5);
getObject() 方法中会调用 getMapper() 方法,从MapperRegistry 中的 knowMappers 集合里拿到对象的代理工厂,然后用它来创建代理对象
1 2 3 4 5 public T newInstance (SqlSession sqlSession) {new MapperProxy (sqlSession, this .mapperInterface, this .methodCache);return this .newInstance(mapperProxy);
总结
mybatis定义一个注解@MapperScan
在@MapperScan中通过@Import导入了MapperScannerRegistrar,使这个类在启动时被加载
在MapperScannerRegistrar类中,先通过Spring扫描得到多个beanDefinition,后由mybatis的processBeanDefinitions() 方法处理上边的多个beanDefinitions
遍历每一个处理后的beanDefinition,并添加构造方法,设置接口名字为bean的类型,至此bean类型确定。
为每一个处理后的beanDefinition,设置FactoryBean(其实就是MapperFactoryBean.class)
在MapperFactoryBean中的getObject()方法中,通过动态代理获取每一个 mapper 的代理对象,因为上文@Import导入了MapperScannerRegistrar,所以这些代理对象在启动时会被加入到容器以供后续随时使用