@Async 是 Spring 框架中用于实现异步方法调用的注解。通过在方法上添加 @Async 注解,可以告诉 Spring 将该方法的执行放到一个独立的线程中,使得方法可以异步执行,而不会阻塞当前线程
在传统的同步方法调用中,当一个方法被调用时,调用者会一直等待方法执行完成,然后才能继续执行后续的操作。而使用 @Async 注解后,方法的执行将变为异步的,调用者可以继续执行后续操作,而方法的执行会在另一个线程中进行
Async 使用 @Async 注解的步骤:
在 Spring 配置文件中开启异步支持或者在启动类上标注 @EnableAsync
在需要异步执行的方法上添加 @Async 注解
示例代码如下:
启用异步支持:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:task ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task.xsd" ><task:annotation-driven /> </beans >
在方法上添加 @Async 注解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service public class MyService {@Async public void asyncMethod () {
在上面的示例中,asyncMethod 方法被 @Async 注解标记,表示该方法会异步执行。当调用 asyncMethod 方法时,Spring 将会在一个独立的线程中执行这个方法,而不会阻塞当前线程
@EnableAsync与@EnableTransactionManagement 类似,向 Spring 导入了 AsyncConfigurationSelector.class 组件,同样属于 ImportSelector 类型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class) public @interface EnableAsync {extends Annotation > annotation() default Annotation.class;boolean proxyTargetClass () default false ;mode () default AdviceMode.PROXY;int order () default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
AsyncConfigurationSelector
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class AsyncConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector <EnableAsync> {@Override @Nullable public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {switch (adviceMode) {case PROXY:return new String [] {ProxyAsyncConfiguration.class.getName()};case ASPECTJ:return new String [] {ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};default :return null ;
一般使用时默认未修改 AdviceMode,故 AsyncConfigurationSelector 向 Spring 容器添加了名为 ProxyAsyncConfiguration 的 bean
ProxyAsyncConfiguration
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public class ProxyAsyncConfiguration extends AbstractAsyncConfiguration {@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.ASYNC_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME) @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor asyncAdvisor () {this .enableAsync, "@EnableAsync annotation metadata was not injected" );AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor bpp = new AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor ();this .executor, this .exceptionHandler);extends Annotation > customAsyncAnnotation = this .enableAsync.getClass("annotation" );if (customAsyncAnnotation != AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(EnableAsync.class, "annotation" )) {this .enableAsync.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass" ));this .enableAsync.<Integer>getNumber("order" ));return bpp;
ProxyAsyncConfiguration 向容器中注入了一个 AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
AbstractAsyncConfiguration 是 ProxyAsyncConfiguration 的父类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 @Configuration public abstract class AbstractAsyncConfiguration implements ImportAware {@Nullable protected AnnotationAttributes enableAsync;@Nullable protected Supplier<Executor> executor;@Nullable protected Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler;@Override public void setImportMetadata (AnnotationMetadata importMetadata) {this .enableAsync = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(false ));if (this .enableAsync == null ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("@EnableAsync is not present on importing class " + importMetadata.getClassName());@Autowired(required = false) void setConfigurers (Collection<AsyncConfigurer> configurers) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {return ;if (configurers.size() > 1 ) {throw new IllegalStateException ("Only one AsyncConfigurer may exist" );AsyncConfigurer configurer = configurers.iterator().next();this .executor = configurer::getAsyncExecutor;this .exceptionHandler = configurer::getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler;
从这里可以看出,可以通过向spring容器中注入AsyncConfigurer 来配置执行异步任务的线程池和异常处理器
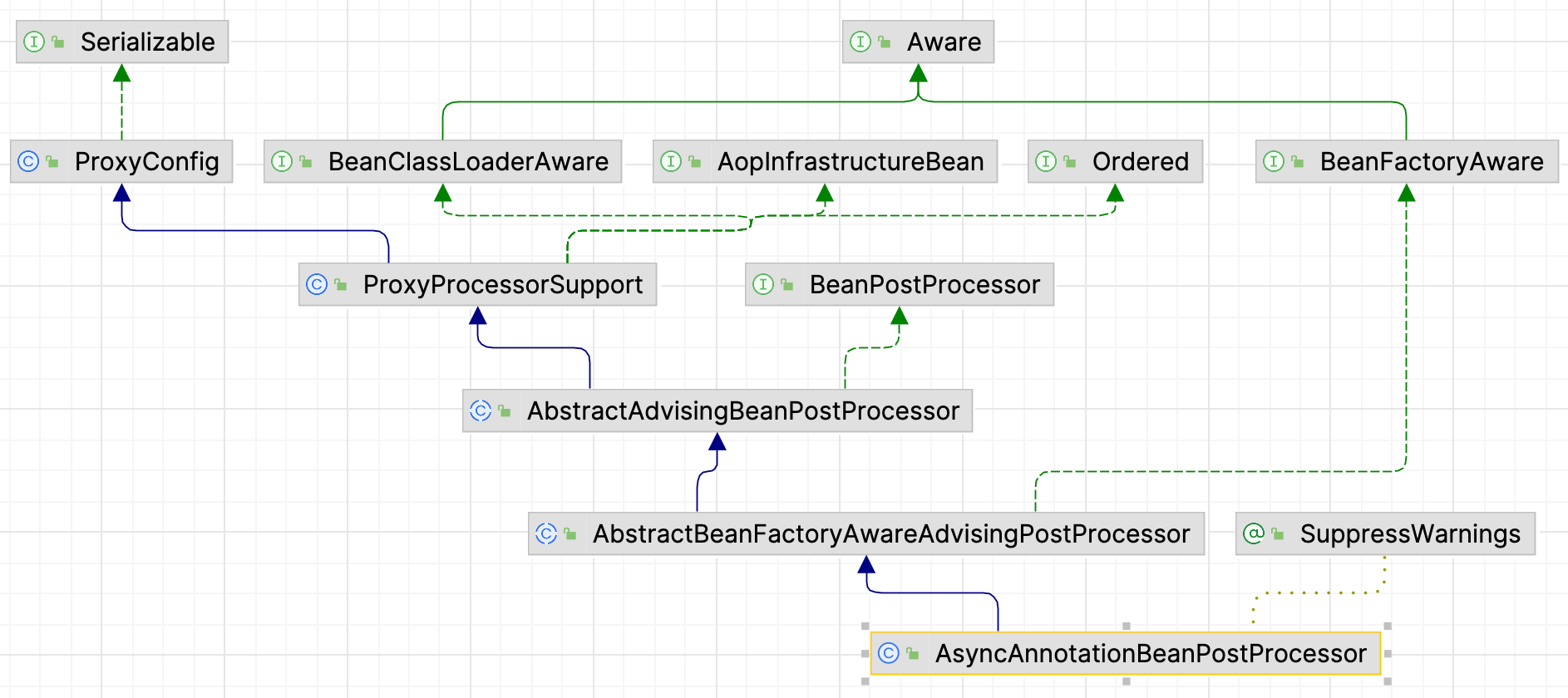
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 主要实现了 BeanFactoryAware 和 BeanPostProcessor 接口
org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#setBeanFactory
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void setBeanFactory (BeanFactory beanFactory) {super .setBeanFactory(beanFactory);AsyncAnnotationAdvisor advisor = new AsyncAnnotationAdvisor (this .executor, this .exceptionHandler);if (this .asyncAnnotationType != null ) {this .asyncAnnotationType);this .advisor = advisor;
在 AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 实例化时实例化了切面 AsyncAnnotationAdvisor
每个 bean 实例化完后都会调用 AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()判断是否要生成代理对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) {if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) {ProxyFactory proxyFactory = prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName);if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {this .advisor);return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());return bean;
AsyncAnnotationAdvisor切面 AsyncAnnotationAdvisor 包括通知 AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor 和切点ComposablePointcut
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public AsyncAnnotationAdvisor ( @Nullable Supplier<Executor> executor, @Nullable Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler) {extends Annotation >> asyncAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet <>(2 );try {extends Annotation >)"javax.ejb.Asynchronous" , AsyncAnnotationAdvisor.class.getClassLoader()));catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {this .advice = buildAdvice(executor, exceptionHandler); this .pointcut = buildPointcut(asyncAnnotationTypes); protected Advice buildAdvice ( @Nullable Supplier<Executor> executor, @Nullable Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler)AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor interceptor = new AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor (null );return interceptor;protected Pointcut buildPointcut (Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes) {ComposablePointcut result = null ;for (Class<? extends Annotation > asyncAnnotationType : asyncAnnotationTypes) {Pointcut cpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut (asyncAnnotationType, true ); Pointcut mpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut (null , asyncAnnotationType, true ); if (result == null ) {new ComposablePointcut (cpc);else {return (result != null ? result : Pointcut.TRUE);
AnnotationMatchingPointcut 切面其实就是查看类或者方法上面有没有 @Async 注解。
AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptorAnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor 类主要负责增强逻辑的实现,继承了 AsyncExecutionInterceptor,其中的 invoke() 实现了增强逻辑
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionInterceptor#invoke
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public Object invoke (final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null );Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);final Method userDeclaredMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);AsyncTaskExecutor executor = determineAsyncExecutor(userDeclaredMethod);if (executor == null ) {throw new IllegalStateException ("No executor specified and no default executor set on AsyncExecutionInterceptor either" );try {Object result = invocation.proceed();if (result instanceof Future) {return ((Future<?>) result).get();catch (ExecutionException ex) {catch (Throwable ex) {return null ;return oSubmit(task, executor, invocation.getMethod().getReturnType());
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionAspectSupport#determineAsyncExecutor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 protected AsyncTaskExecutor determineAsyncExecutor (Method method) {AsyncTaskExecutor executor = this .executors.get(method);if (executor == null ) {String qualifier = getExecutorQualifier(method);if (StringUtils.hasLength(qualifier)) {this .beanFactory, qualifier);else {this .defaultExecutor.get();if (targetExecutor == null ) {return null ;instanceof AsyncListenableTaskExecutor ?new TaskExecutorAdapter (targetExecutor));this .executors.put(method, executor);return executor;
determineAsyncExecutor() 负责获取异步任务执行的线程池,线程池的查找步骤如下:
从Spring容器中寻找 @Async 注解中的value属性中指定的 taskExecutor
寻找默认的 defaultExecutor
默认的 defaultExecutor 来自于
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionAspectSupport#configure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void configure (@Nullable Supplier<Executor> defaultExecutor, @Nullable Supplier<AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler> exceptionHandler) {this .defaultExecutor = new SingletonSupplier <>(defaultExecutor, () -> getDefaultExecutor(this .beanFactory));this .exceptionHandler = new SingletonSupplier <>(exceptionHandler, SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler::new );
defaultExecutor首先取参数传入的defaultExecutor,这个参数来自接口AsyncConfigurer.getAsyncExecutor(),如果参数为null,那么就调用getDefaultExecutor(),注意这个方法子类AsyncExecutionInterceptor重写了:
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionInterceptor#getDefaultExecutor
1 2 3 4 protected Executor getDefaultExecutor (@Nullable BeanFactory beanFactory) {Executor defaultExecutor = super .getDefaultExecutor(beanFactory);return (defaultExecutor != null ? defaultExecutor : new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor ());
如果找不到defaultExecutor就会创建一个SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor
再来看看父类的 AsyncExecutionAspectSupport#getDefaultExecutor:
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionAspectSupport#getDefaultExecutor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 protected Executor getDefaultExecutor (@Nullable BeanFactory beanFactory) {if (beanFactory != null ) {try {return beanFactory.getBean(TaskExecutor.class);catch (NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException ex) {"Could not find unique TaskExecutor bean" , ex);try {return beanFactory.getBean(DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME, Executor.class);catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {"More than one TaskExecutor bean found within the context, and none is named " +"'taskExecutor'. Mark one of them as primary or name it 'taskExecutor' (possibly " +"as an alias) in order to use it for async processing: " + ex.getBeanNamesFound());catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {"Could not find default TaskExecutor bean" , ex);try {return beanFactory.getBean(DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME, Executor.class);catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {"No task executor bean found for async processing: " +"no bean of type TaskExecutor and no bean named 'taskExecutor' either" );return null ;
先从beanFactory中获取TaskExecutor类型的对象,然后再找名为taskExecutor的Executor对象
org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionAspectSupport#doSubmit
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 protected Object doSubmit (Callable<Object> task, AsyncTaskExecutor executor, Class<?> returnType) {if (CompletableFuture.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {return task.call();catch (Throwable ex) {throw new CompletionException (ex);else if (ListenableFuture.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {return ((AsyncListenableTaskExecutor) executor).submitListenable(task);else if (Future.class.isAssignableFrom(returnType)) {return executor.submit(task);else {return null ;
doSubmit() 负责将任务提交至线程池中,并对各种方法的返回值进行处理
Spring 定义的线程池类 Spring 已经定义的线程池类有如下一些:
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor:不是真的线程池,这个类不重用线程,默认每次调用都会创建一个新的线程SyncTaskExecutor:这个类没有实现异步调用,只是一个同步操作。只适用于不需要多线程的地方ConcurrentTaskExecutor:Executor的适配类,不推荐使用。如果 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 不满足要求时,才用考虑使用这个类SimpleThreadPoolTaskExecutor:是Quartz的 SimpleThreadPool 的类。线程池同时被quartz和非quartz使用,才需要使用此类ThreadPoolTaskExecutor :最常使用,推荐。 其实质是对java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor 的包装
配置自定义线程池 异步方法默认的线程池 在 @EnableAsync 注解中有如下注释说明:
By default, Spring will be searching for an associated thread pool definition:either a unique {@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor} bean in the context,or an {@link java.util.concurrent.Executor} bean named “taskExecutor” otherwise. Ifneither of the two is resolvable, a {@link org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor}will be used to process async method invocations.
翻译一下就是:
Spring首先会通过下面两种方式查找作为异步方法的默认线程池:
而 SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor 线程池去执行 @Async 标注的异步方法,由于该线程池不会重用线程,所以项目中推荐使用自定义的线程池。
配置异步方法默认自定义线程池 配置 @Async 默认的线程池有多种方式:
重新实现接口 AsyncConfigurer
继承 AsyncConfigurerSupport
自定义一个 TaskExecutor 类型的bean
自定义一个名称为 taskExecutor 的Executor类型的Bean
实现接口
开发者可以通过实现 AsyncConfigurer 接口来自定义自己的线程池,以下是官方文档给的例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Configuration @EnableAsync public class AppConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {@Override public Executor getAsyncExecutor () {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor ();7 );42 );11 );"MyExecutor-" );return executor;@Override public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler () {return new MyAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler ();
继承类
通过继承 AsyncConfigurerSupport 类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Configuration public class AppConfig extend AsyncConfigurerSupport {@Override @Bean public Executor getAsyncExecutor () {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor ();7 );42 );11 );"MyExecutor-" );return executor;@Override public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler () {return new MyAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler ();
配置自定义的TaskExecutor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Configuration public class AppConfig {@Override @Bean(name=AsyncExecutionAspectSupport.DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME) public Executor taskExecutor () {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor ();7 );42 );11 );"MyExecutor-" );return executor;
不同异步方法配置不同线程池
有时候不同功能的异步方法需要配置不同的线程池,可以通过在 @Async 上指定线程池的名称来实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 @Configuration public class ExecutorConfig {@Bean("customExecutor-1") public Executor customExecutor1 () {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor ();3 );6 );60 );10 );"customExecutor-1-" );new ThreadPoolExecutor .AbortPolicy());true );return executor;@Bean("customExecutor-2") public Executor customExecutor2 () {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor ();3 );6 );60 );10 );"customExecutor-2-" );new ThreadPoolExecutor .AbortPolicy());true );return executor;@Async("customExecutor-1") public void method1 () {}@Async("customExecutor-2") public void method2 () {}
@Async 异常处理当方法是带Future返回值的时候,Future.get()方法会抛出异常,所以异常捕获是没问题的。但是当方法是不带返回值的时候,那么此时主线程就不能捕获到异常,需要额外的配置来处理异常,可以有下面两种方式。
通过try-catch处理异常
直接在异步方法中使用 try-catch 来处理抛出的异常。这个方法也可以用于带 Future 返回值的异步方法。
通过实现 AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler 接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Configuration @EnableAsync public class SpringAsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {@Override public Executor getAsyncExecutor () {@Override public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler () {return new AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler () {@Override public void handleUncaughtException (Throwable throwable, Method method, Object... objects) {"发生异常!异常原因:" + throwable.getMessage() );
注意
@Async 注解必须用在 public 访问级别的方法上,因为 Spring 使用代理来实现异步调用,所以只有 public 方法才能被代理
异步方法的返回值类型通常应该是 void 或 java.util.concurrent.Future。如果返回 Future 类型,则可以通过 Future 对象来获取异步方法的执行结果
异步方法应该在不同的类中调用,这样 Spring 能够正确地创建一个独立的线程来执行异步方法。
需要配置一个合适的 TaskExecutor,用于执行异步任务。如果没有配置,Spring 将使用默认的 SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor
总结来说,@Async 注解是 Spring 框架中实现异步方法调用的一种方式,它提供了一种简单的方法来实现多线程处理,从而提高应用程序的并发能力和性能